Hot Topics //
-

Assista TV grátis sem assinatura
Usando os aplicativos abaixo, assista TV grátis sem assinatura e tenha acesso a todos os canais de TV do mundo…
-
Assista TV grátis sem assinatura
Usando os aplicativos abaixo, assista TV grátis sem assinatura e tenha acesso a todos os canais de TV do mundo…
-
Cricket ao vivo grátis pelo app
Assista a partidas de cricket ao vivo grátis pelo app e tenha um acesso exclusivo a todas as transmissões dos…
-
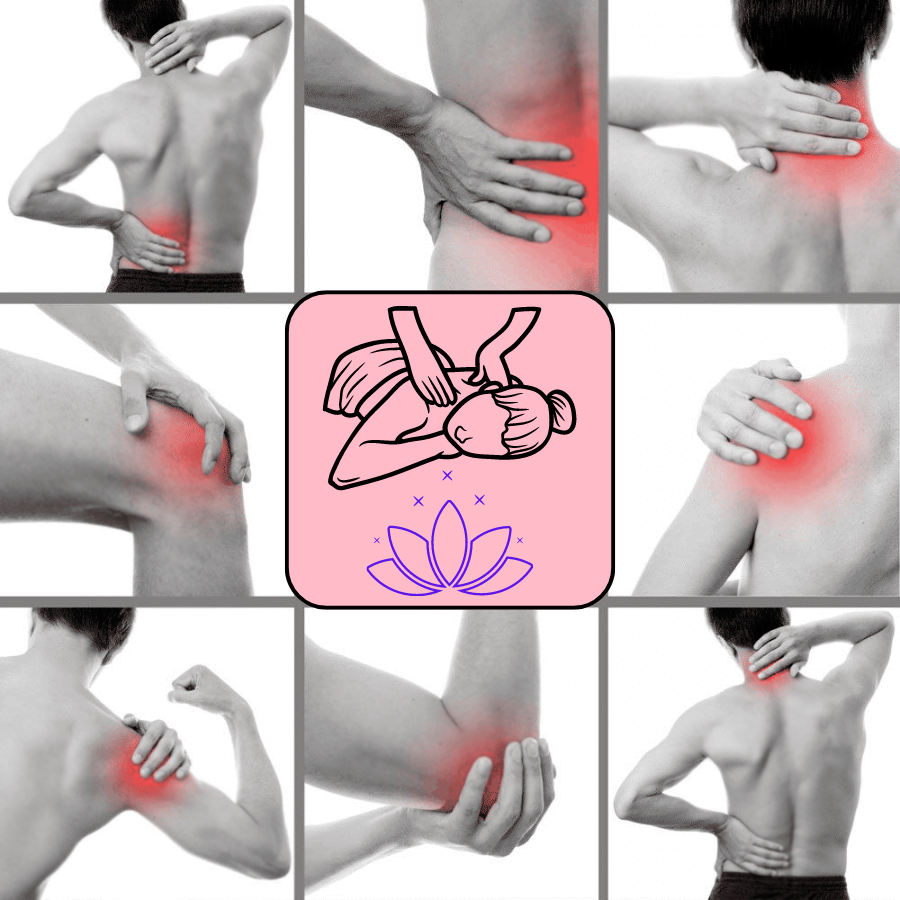
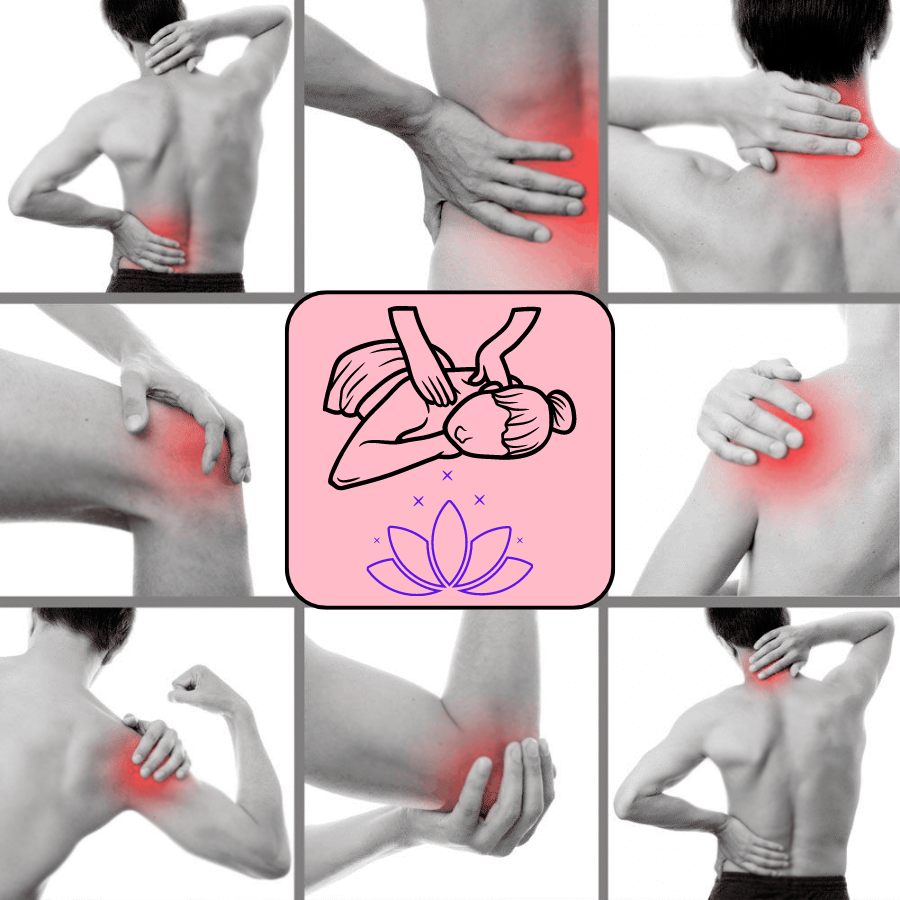
Aprenda a fazer massagem com aplicativo grátis
Aprenda a fazer massagem com aplicativo grátis e se torne um profissional com técnicas avançadas que você aprende nos apps…
-
Aprenda a fazer massagem com aplicativo grátis
Aprenda a fazer massagem com aplicativo grátis e se torne um profissional com técnicas avançadas que você aprende nos apps…
-
Melhores aplicativos para ver notícias urgentes
Confira aqui os melhores aplicativos para ver notícias urgentes no seu celular, veja agora o que está acontecendo de mais…
-
Aplicativo seguro e gratuito para espionar WhatsApp
Monitore conversas dos seus filhos ou da pessoa que você ama através deste aplicativo para espionar WhatsApp de forma segura.…
-
NFL ao vivo e sem travar totalmente grátis
Assista a NFL ao vivo e sem travar totalmente grátis usando o seu celular com a ajuda dos melhores aplicativos…
-
Câmeras ao vivo diretamente das praias
Veja as câmeras ao vivo diretamente das praias e verifique se está lotada, se está com muitas ondas para que…